Boulder Opal vs Agate – 3 Key Differences to Know
You've likely heard of Boulder Opal and Agate, two unique gemstones with distinct origins and characteristics. Perhaps you've marveled at the Boulder Opal's vibrant play-of-color, or admired the Agate's mesmerizing banding patterns.
But have you ever wondered about the differences between these two stones, from their formation to their usage? As you explore these gemstones further, you'll begin to appreciate the unique beauty and significance each one brings to the world of jewelry and crystal therapy. So, are you ready to unravel the mysteries of Boulder Opal and Agate?
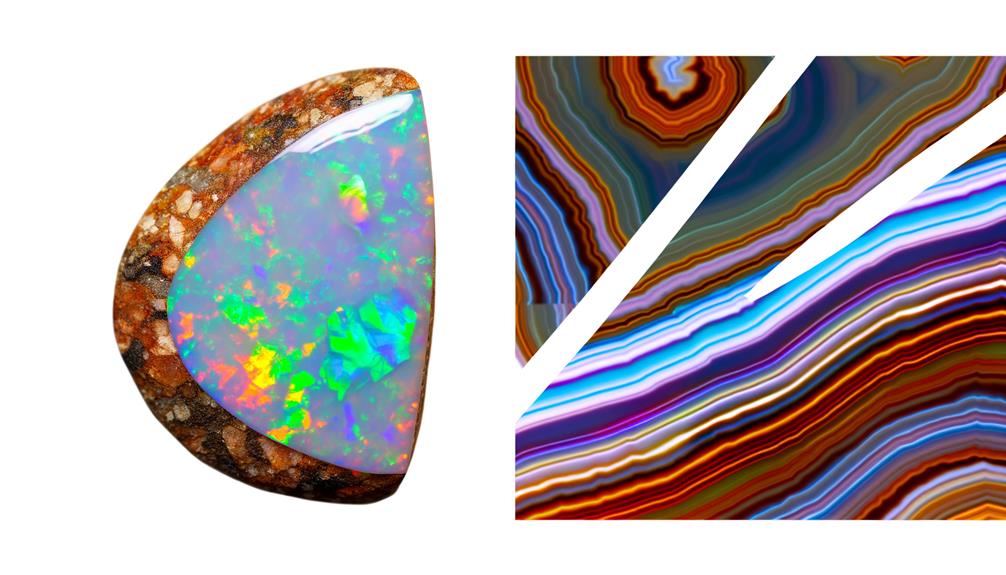
Key Takeaways
- Boulder Opals, formed in ironstone boulders in Australia, are known for their vibrant play-of-color and durability.
- Agates, found globally in volcanic rocks, are recognized for their unique banding patterns and variety of colors.
- Boulder Opals are sought after for their rarity and beauty in jewelry and decorative art, while Agates are popular in home decor and crystal therapy.
- Boulder Opals' value is determined by color vibrancy and pattern, whereas Agate's allure lies in its translucency and unique banding.
- Agate has a higher hardness level, ranking 7 on the Mohs scale, making it suitable for precision use in scientific instruments.
Understanding Gemstones: Boulder Opal
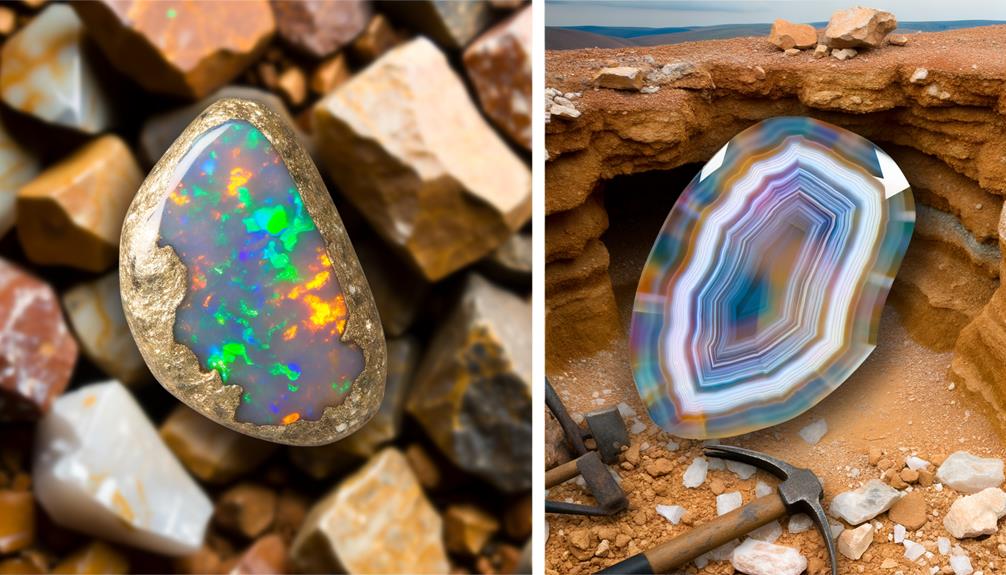

Diving into the world of gemstones, you'll find Boulder Opal, a unique type with a vibrant play of color, isn't just a stone, but a visual spectacle that sets it apart in the domain of precious gems.
Unlike other opals, Boulder Opals are formed in ironstone boulders, which serve as a natural backing, enhancing their durability. You'll love the brilliant play-of-color against the dark, earthy ironstone. This contrast is what makes Boulder Opals so striking and desirable.
Their color range is vast, including shades of blue, green, and even red. The value of Boulder Opals depends on the vibrancy and pattern of these colors. As a gem enthusiast, understanding Boulder Opals' aesthetics and physical properties is essential, offering you a deeper comprehension of their uniqueness.
Origin and Formation of Boulder Opal
To truly appreciate Boulder Opals, you need to explore their origin and understand their unique formation process. These stunning gemstones hail from Queensland, Australia, where they form over millions of years in ironstone boulders.
Here's a simplified sequence of their formation:
- Water carrying silica solution seeps into crevices in ironstone boulders.
- Over time, the solution solidifies into opal.
- The opal forms within the boulder, hence the name 'Boulder Opal'.
This intricate process results in a gemstone that's both beautiful and sturdy. It's fascinating, isn't it? How nature works its magic, turning simple ingredients into a marvel.
But remember, this is a simplified explanation. The actual formation process involves complex geological phenomena.
Unique Characteristics of Boulder Opal
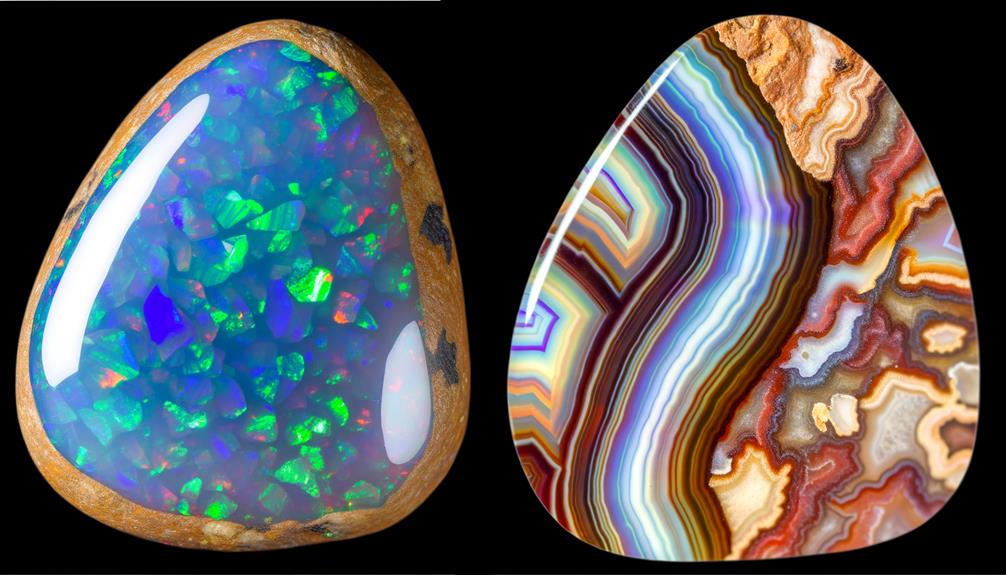
While you may already be interested in the formation process of Boulder Opals, it's their unique characteristics that truly set them apart in the world of gemstones.
Unlike other opals, Boulder Opals are formed within ironstone boulders, giving them a distinctive solidity and weight. This unique formation contributes to their stunning color play, which features a dazzling array of hues from fiery reds and oranges to deep blues and greens. Each stone is a one-of-a-kind spectacle of color, no two are exactly alike.
Boulder Opals also have a natural layer of ironstone on the back, which not only adds to their durability but also enhances the vibrancy of their color play. Essentially, these characteristics make Boulder Opals a captivating choice for gemstone enthusiasts.
Common Uses of Boulder Opal
You'll often find Boulder Opal used in various forms of jewelry, from rings and necklaces to bracelets and earrings, thanks to its striking color play and durability. Its unique, vibrant hues and patterns make it a highly sought-after gemstone, especially for high-end, custom-made pieces.
Jewelry: Boulder Opal is a favorite in the jewelry industry. Its dazzling play of colors adds an air of sophistication and uniqueness to any piece.
Collectibles: Due to their rarity and beauty, Boulder Opals often form part of gemstone collections. They're prized by both amateur and professional collectors.
Artistic Creations: Artists and craftsmen use Boulder Opals in various forms of decorative art, from sculptures to inlays, adding a touch of luxury and elegance.
Gems Uncovered: The Agate Stone
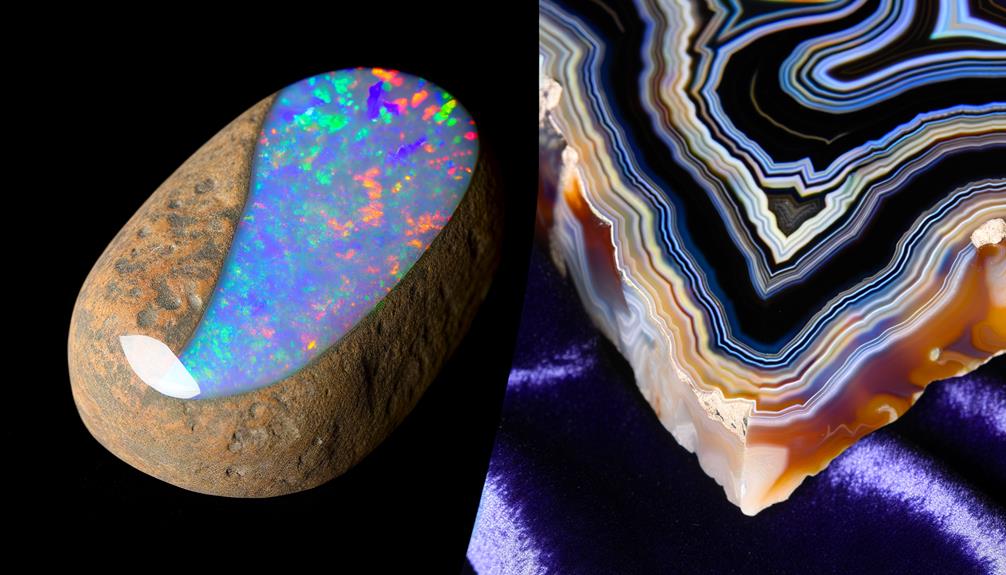

Peeling back the layers of the gemstone world, let's uncover the Agate, a stone renowned for its stunning bands of color and remarkable durability. Each individual Agate carries its unique signature, a fascinating blend of hues and patterns, making it a favorite among gemstone enthusiasts and jewelers alike.
Agate isn't just a feast for the eyes. It's also a hardy gem, ranking 7 on the Mohs hardness scale, making it resistant to scratches and everyday wear-and-tear. Additionally, it possesses a translucent quality that adds depth to its vivid palette, enhancing its allure.
Agate's beauty and durability aren't its only draws. It also boasts a rich history, with cultural significance in various societies. From ancient times to today, it's treasured for its aesthetic and symbolic value.
Formation Process of Agate
Now, let's turn your focus to the formation process of Agate.
You'll discover the intricate geological creation of this unique gemstone, shaped and influenced by various elements over time.
Agate's Geological Creation
Delving into the geological creation of agate, it's important to understand that these semi-precious gemstones form over millions of years, slowly crystallizing within volcanic rocks or ancient lavas where silica-rich groundwater percolates.
This process involves several intricate and fascinating steps:
- Silica-rich groundwater infiltration: The first step involving the seeping of silica-rich groundwater into cavities and fractures of volcanic rocks or ancient lavas.
- Silica deposition: The second step is the deposition of silica layers onto the walls of the cavities, starting the formation of agates.
- Crystallization: The last step involves the slow crystallization of silica over millions of years, resulting in the formation of these beautiful and unique gemstones.
Elements Influencing Agate Formation
Understanding the formation process of agate isn't enough, you also need to take into account the various elements that influence this formation, adding complexity and diversity to these unique gemstones.
For instance, the mineral composition of the host rock is critical; it largely determines the color and banding patterns seen in agates.
The temperature and pressure conditions during formation also play key roles, impacting the crystallization process.
In addition, the presence of water in the environment is pivotal, as it facilitates the transportation and deposition of silica, the primary constituent of agate.
Moreover, the rate at which the silica-rich solution cools and solidifies can influence the size and clarity of the agate's microcrystalline structures, adding another layer of complexity to its formation.
Distinct Features of Agate
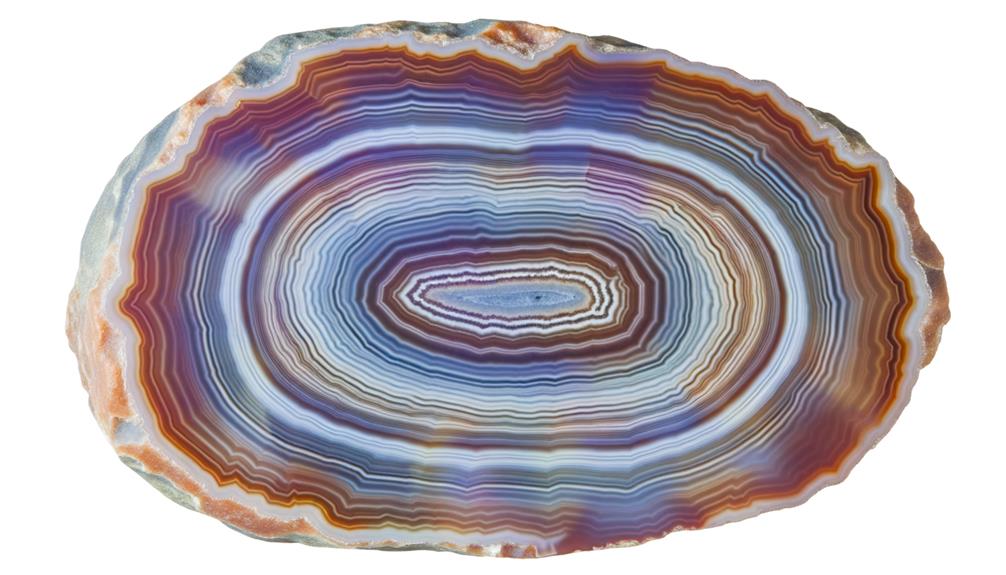

Agate stands out for its unique formation process, which we'll discuss first.
You'll be fascinated by how its vibrant color variations come about, making each piece truly unique.
We'll also touch on the symbolic and healing properties of agate which make it more than just a pretty stone.
Agate's Unique Formation Process
To truly appreciate the beauty of Agate, understanding its unique formation process is essential, a tribute to the intricate workings of nature over millions of years. This process occurs in stages within volcanic rock or ancient lavas where cavities have formed.
First, water rich in silica fills these cavities or vesicles.
Over time, the water begins to evaporate, leaving behind a silica deposit. This forms the initial layer of Agate.
This process repeats over centuries, creating concentric bands of silica.
This cyclical, meticulous process results in the unique, layered look of Agate. It's a demonstration of the enduring power of nature and time, working together to create something truly beautiful.
The Color Variations in Agate
Diving into the distinct features of Agate, you'll find that its color variations stand out remarkably, with hues ranging from rich earthy browns to vibrant pinks and blues. This color diversity is due to the various impurities and mineral inclusions within the stone.
Iron oxides, for example, impart a range of reds, yellows, and browns. Copper can produce blues and greens, while manganese contributes purples and pinks.
This plethora of colors often forms bands, which are the signature characteristic of Agate. They can appear as concentric rings or in irregular patterns, creating a visual feast that's truly unique to each piece. These variations not only make Agate aesthetically pleasing but also contribute to its identification and classification.
Agate's Symbolic and Healing Properties
Delving deeper into the distinct features of Agate, it's worth noting that the stone isn't just admired for its visual appeal, but also for its significant symbolic and healing properties.
Symbolic Properties:
Agate is often seen as a stone of strength. It's believed to promote courage and resilience, helping you to tackle challenges head-on.
Emotional Healing:
Agate is said to soothe and calm, helping to alleviate tension and inner anger. It's a stone that encourages positive self-reflection, fostering feelings of self-acceptance and confidence.
Physical Healing:
Some followers of crystal healing attribute Agate with improving digestive health and boosting physical endurance.
How Agate Is Utilized
You'll find that agate, a versatile and widely appreciated gemstone, is used in a variety of applications ranging from jewelry making to home decor, and even in some scientific instruments due to its unique properties.
As a jewelry staple, agate provides a stunning range of colors and banding patterns that make each piece visually unique. Its durability allows it to be cut and polished into beads, pendants, or cabochons.
In home decor, agate's vibrant hues and natural patterns are utilized in decorative items such as coasters, bookends, and lamp bases.
Notably, its inherent hardness and stability qualify it for precision use in certain scientific instruments.
Boulder Opal Vs Agate: A Comparison
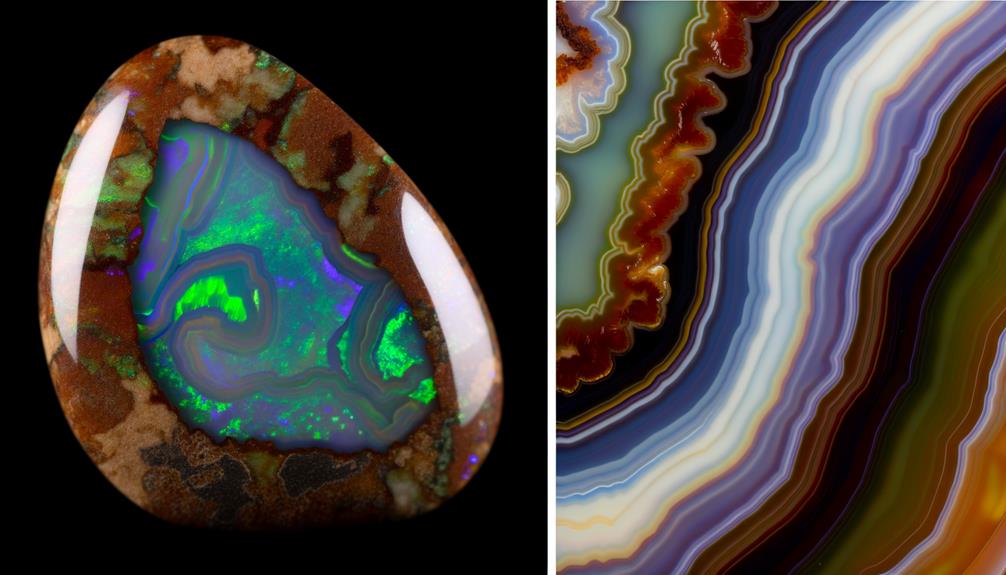
Let's compare Boulder Opal and Agate, two magnificent gemstones, each possessing unique characteristics that set them apart in the world of gemology.
- Origin: Boulder Opal, native to Australia, forms in ironstone boulders. Agate, on the other hand, occurs globally in volcanic rocks and metamorphic rocks.
- Appearance: Boulder Opals are renowned for their vibrant play-of-color, displaying a spectrum of hues. Agates are attractive for their banding patterns and variety of colors.
- Uses: Boulder Opal is highly sought after for jewelry due to its unique color play. Agate, used in jewelry as well, is also popular for its healing properties in crystal therapy.
Understanding these key differences can enhance your appreciation for these gemstones and their unique qualities.
Conclusion
So, you've explored the realm of Boulder Opal and Agate, each possessing their unique charm.
Boulder Opal, with its enchanting color play, mesmerizes endlessly.
Agate, on the other hand, impresses with its mesmerizing bands and healing abilities.
Both gems, though distinct in their own way, share a common thread – they're nature's masterworks, crafted to charm and fascinate.
Whether you're a jeweler, a healer, or a gem enthusiast, they're treasures worth cherishing.






