Key Differences Between Chocolate Opals and Fire Agate: 7 Things to Know
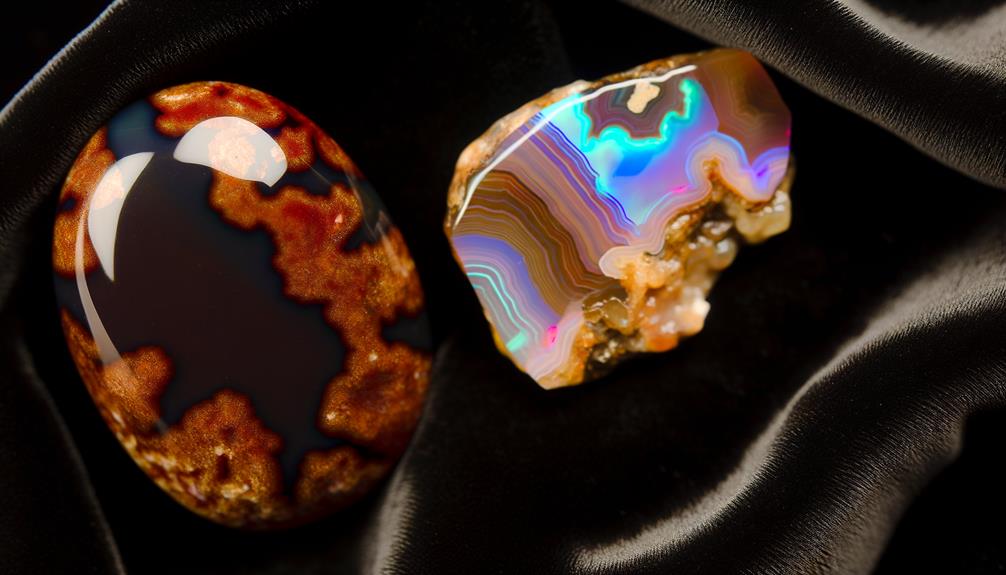
No, chocolate opals and fire agates aren't the same. Chocolate opals form in volcanic regions with silica-rich solutions, displaying rich earthy tones due to iron oxide impurities.
Fire agates, however, originate in hydrothermal environments and show vibrant iridescent flashes from layers of chalcedony and iron oxide. The internal structures of these gemstones result in distinct play-of-color patterns.
Physically, chocolate opals are softer, with a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6.5, while fire agates are harder, ranging from 6.5 to 7. To uncover more specific details and differences, you'd want to look into their geological and mineralogical properties further.

Key Takeaways
- Chocolate opals and fire agates have different geological formations, with chocolate opals forming in volcanic regions and fire agates in hydrothermal environments.
- The color of chocolate opals is mainly brown and red, while fire agates display vibrant iridescent colors like orange, red, and brown.
- Chocolate opals feature a play of color due to silica spheres, whereas fire agates derive their iridescence from chalcedony and iron oxide layers.
- Chocolate opals are softer with a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6.5, compared to fire agates which range from 6.5 to 7.
- Both gemstones have unique mineral compositions, contributing to their distinct appearances and physical properties.
Formation Process
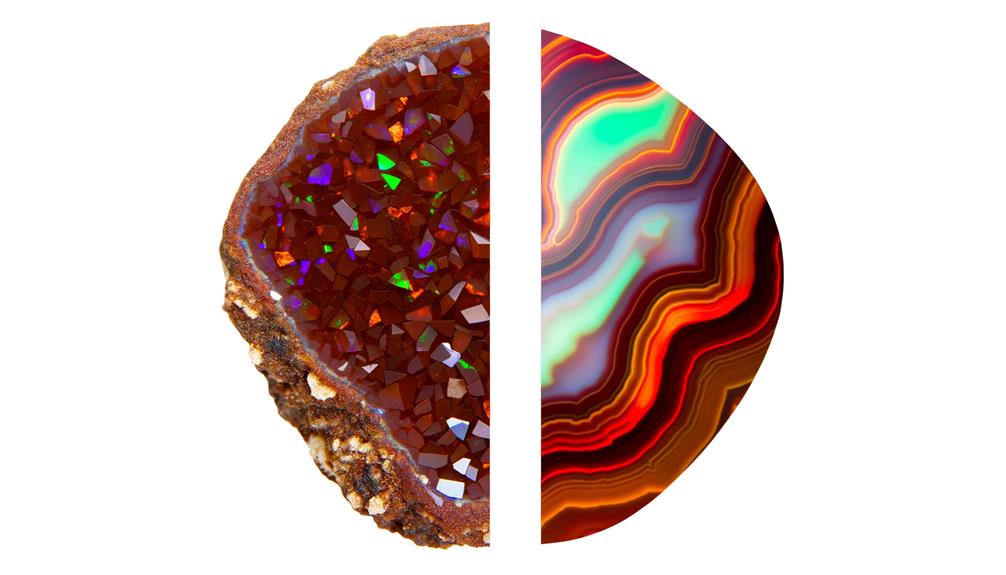
The formation process of chocolate opals involves the deposition of silica spheres in a hydrated environment over millions of years.
You'll find that these silica spheres, present in a colloidal suspension, gradually settle and form intricate layers.
The hydration aspect is essential as it aids in the diffusion of silica particles, enabling the formation of microscopic, uniform spheres.
These spheres then stack in a tightly packed grid, which results in the opal's characteristic play-of-color.
This meticulous stacking and layering process is influenced by the surrounding geological conditions, including temperature and pressure variations.
Understanding this process helps you appreciate the uniqueness and complexity of chocolate opals, distinguishing them from other opal varieties and gemstones.
Geological Origins
Understanding the formation process lays the groundwork for exploring the geological origins of chocolate opals and fire agate, which are intrinsically tied to their unique environmental conditions and mineral compositions.
Chocolate opals typically form in volcanic regions where silica-rich solutions permeate cracks in the host rock, subsequently solidifying as opal. This environment fosters the formation of hydrated amorphous silica, contributing to their distinct appearance.
Fire agate, on the other hand, originates in hydrothermal environments where silica and iron oxide solutions infiltrate cavities in volcanic rocks. The unique interplay of silica gel and iron oxide layers creates the distinctive iridescence seen in fire agate.
Both gemstones' geological contexts greatly influence their mineralogical properties and overall formation, making each unique in its own right.
Color Variations
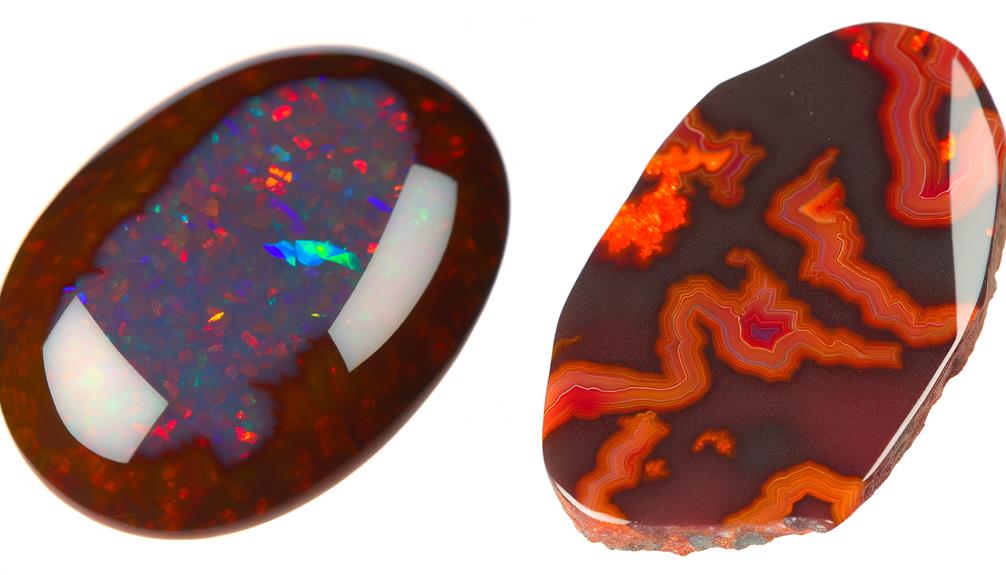
You'll observe that Chocolate Opals exhibit rich earthy tones, often in shades of brown and red, while Fire Agate displays a vibrant color play with iridescent flashes.
Chocolate Opals typically present a more uniform coloration, whereas Fire Agate boasts unique pattern differences due to its layered formation.
These distinct color variations result from differing mineral compositions and structural formations.
Rich Earthy Tones
Chocolate opals and fire agate exhibit a mesmerizing array of rich earthy tones, showcasing unique color variations that stem from their distinct mineral compositions.
In chocolate opals, you'll observe deep browns interspersed with subtle reds and oranges, resulting from the presence of iron oxide impurities.
Fire agate, on the other hand, displays a spectrum of reds, browns, and golds, attributed to the layered formation of chalcedony and iron oxide. These tones arise due to light interference within the microcrystalline structure.
Vibrant Color Play
The intricate interplay of light within chocolate opals and fire agate leads to vibrant color play, where you'll observe flashes of greens, blues, and purples among the earthy tones.
In chocolate opals, the phenomenon known as 'play-of-color' occurs due to the diffraction of light by silica spheres. You'll notice a spectral display of colors that shift with the angle of light incidence.
Fire agate, on the other hand, exhibits its iridescence through interference and diffraction within its chalcedony layers. Here, the vibrant hues result from the thin film interference of light reflecting off layered inclusions.
Both stones offer an enthralling visual experience, yet the underlying mechanisms behind their color variations are distinct and scientifically intriguing.
Unique Pattern Differences
In comparing the unique pattern differences between chocolate opals and fire agate, you'll observe distinct color variations that arise from their respective internal structures.
Chocolate opals exhibit a play of color due to the diffraction of light through silica spheres of various sizes. This results in vibrant flashes of red, green, and blue against a dark brown matrix.
Fire agate, on the other hand, displays an iridescence caused by the interference of light on thin layers of limonite and silica. Its patterns are more intricate, often resembling flames or plumes, with rich hues of orange, red, and brown.
These color variations are inherently linked to their geological formation processes, which distinctly set chocolate opals apart from fire agate.
Unique Patterns
Have you ever noticed how the intricate patterns in chocolate opals and fire agate result from unique geological processes? Their formation involves distinct mineralogical conditions and environmental factors. Chocolate opals, with their mesmerizing play-of-color, arise from silica deposits in volcanic ash layers. Fire agate, however, derives its stunning iridescence from iron oxide layers interspersed within chalcedony.
| Gemstone | Pattern Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Chocolate Opal | Play-of-color due to silica spheres |
| Fire Agate | Iridescence from iron oxide layers |
These patterns aren't merely aesthetic; they reflect the gemstones' geological history. By examining these structures, you can gain insights into the environmental conditions that existed during their formation. This understanding underscores the uniqueness and value of both chocolate opals and fire agate.
Physical Properties
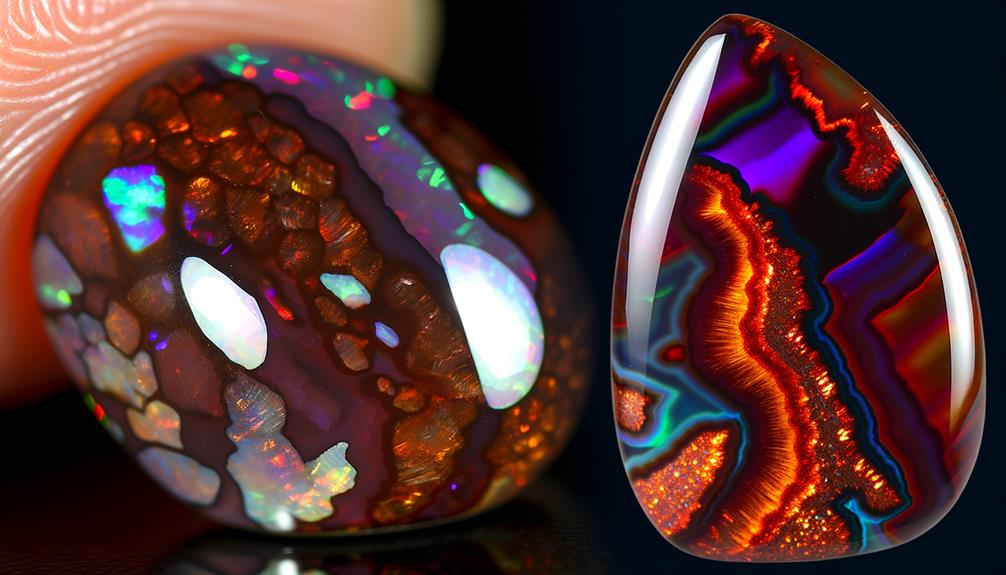

When examining the physical properties of chocolate opals and fire agate, you'll want to focus on color and appearance, hardness and durability, and formation and structure.
Chocolate opals exhibit a rich brown hue with potential for iridescent play-of-color, while fire agate features a more complex iridescence due to its layered quartz and iron oxide composition.
Additionally, understanding their respective hardness on the Mohs scale and structural formation processes will provide deeper insights into their durability and aesthetic appeal.
Color and Appearance
Although both chocolate opals and fire agates showcase a variety of captivating hues, their distinct color patterns and optical phenomena set them apart notably.
Chocolate opals often exhibit a rich, brown base with flashes of vibrant colors due to their play-of-color phenomenon. In contrast, fire agates feature a spectrum of shimmering colors caused by light interference within the stone's layered structure.
Chocolate opals' play-of-color arises from silica spheres creating diffraction. Fire agates' iridescence is a result of thin-film interference within iron oxide layers.
Chocolate opals typically have a more uniform background color compared to the diverse, striped appearance of fire agates.
Understanding these differences helps in recognizing the exceptional beauty and intricate nature of each gemstone.
Hardness and Durability
Beyond their captivating colors, understanding the hardness and toughness of chocolate opals and fire agates is crucial to appreciating their physical properties and suitability for various applications.
Chocolate opals, with a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6.5, are relatively softer and require careful handling to prevent scratches and fractures. In contrast, fire agates boast a higher hardness, typically around 6.5 to 7 on the Mohs scale, making them more resistant to wear and tear.
Durability is also influenced by internal structures; chocolate opals are prone to cracking due to their water content. Fire agates, composed primarily of chalcedony, exhibit greater structural integrity.
When choosing between these gemstones for jewelry or other uses, consider their differing hardness and toughness to guarantee longevity and aesthetic preservation.
Formation and Structure
The formation of chocolate opals involves the deposition of silica spheres in a hydrated matrix. This results in a more uniform structure due to the spherical arrangement of silica. On the other hand, fire agates develop through the layering of silica and iron oxide within chalcedony, creating a distinctive layered pattern. Fire agates exhibit iridescence from the interference and diffraction of light due to their unique layered structure.
- Silica Spheres: Chocolate opals consist of tightly packed silica spheres in a gel-like matrix.
- Layering: Fire agates form by repeated deposition of silica and iron oxide, creating intricate layers.
- Iridescence: Fire agate's characteristic play-of-color arises from light interacting with its layered structure.
Understanding these differences helps in appreciating each gemstone's unique beauty and characteristics.
Optical Phenomena
Chocolate opals and fire agate exhibit distinct optical phenomena due to their unique internal structures and compositions.
In chocolate opals, the play-of-color effect arises from the diffraction of light through silica spheres arranged in a grid-like pattern. This diffraction produces vibrant flashes of color, creating an almost holographic appearance. You'll notice that chocolate opals have a smooth, glassy surface, enhancing their brilliance.
On the other hand, fire agate displays iridescence due to its layered composition of chalcedony and iron oxide. Light interferes with these layers, resulting in a fiery, rainbow-like glow. Fire agate's surface is often irregular, concentrating its iridescent effects in specific areas.
Understanding these phenomena helps you appreciate the unique beauty of each gemstone.
Rarity and Value
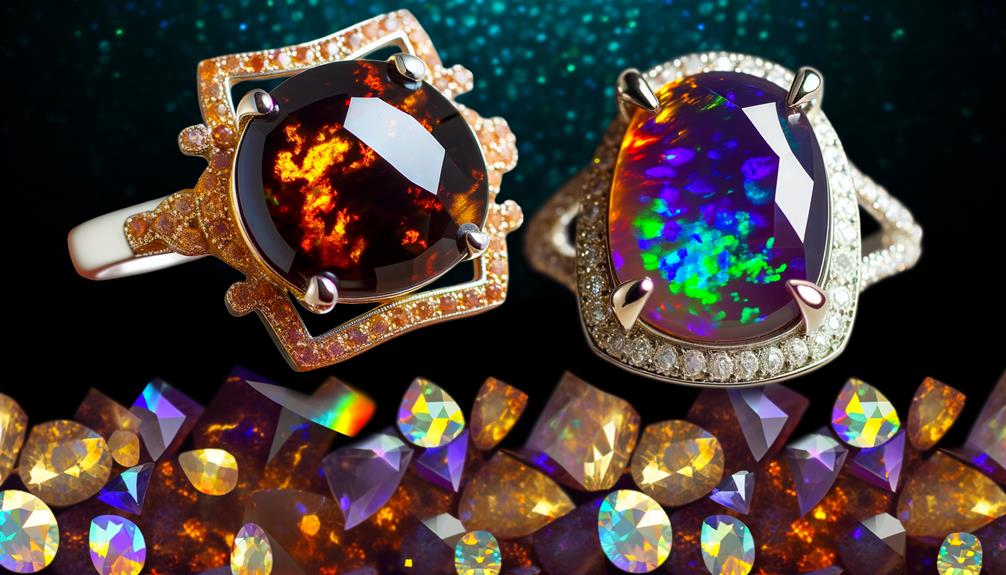

You'll find that rarity and value depend heavily on the geological scarcity and unique optical properties of chocolate opals and fire agate.
Chocolate opals, primarily found in Ethiopia, are rarer due to their limited geographic distribution.
Fire agate, sourced mainly from the southwestern United States and Mexico, owes its value to its intricate iridescence and scarcity.
Key factors influencing their value include:
- Geological Occurrence: Limited mining locations enhance rarity.
- Optical Phenomena: Unique visual effects such as play-of-color in opals and iridescence in fire agate.
- Market Demand: High demand and low supply drive up prices.
Common Uses
You'll find that both chocolate opals and fire agate are extensively utilized in three primary areas: jewelry and accessories, healing and metaphysical practices, and decorative collectibles.
Their unique optical properties make them highly sought after for creating visually striking pieces. Additionally, enthusiasts often attribute various metaphysical and healing properties to these minerals, enhancing their appeal beyond aesthetic value.
Jewelry and Accessories
In the world of jewelry and accessories, both chocolate opals and fire agate are prized for their unique visual properties and durability. When you're selecting pieces, consider how each stone's characteristics can enhance your collection.
Chocolate opals exhibit a rich, dark hue with vibrant flashes, making them ideal for elegant settings. Ideal for high-end, statement jewelry pieces.
Fire agate, on the other hand, offers a fiery glow due to its iridescence and intricate banding. Perfect for intricate designs, often favored in artisan crafts.
Both stones are suitable for everyday wear but require proper care to maintain their luster.
Healing and Metaphysical
Chocolate opals' grounding energy and fire agate's protective properties make them popular in healing and metaphysical practices.
You'll find that chocolate opals are often utilized for their stabilizing influence, promoting emotional balance and resilience. Their energy is believed to anchor you, fostering a sense of calm and security.
Fire agate, on the other hand, is acclaimed for its powerful protective aura. It's thought to act as a shield against negative energies and psychic attacks, enhancing your essentiality and courage.
Both stones are frequently employed in meditation and energy work, where their distinct properties can complement various spiritual and therapeutic objectives.
Decorative Collectibles
Collectors and enthusiasts frequently cherish chocolate opals and fire agates for their striking aesthetic qualities and unique geological formations. You'll find these gemstones not only visually enchanting but also valuable additions to your collection. Their allure stems from their distinct visual properties and intricate internal structures.
- Chocolate Opals: Known for their deep, rich hues and play-of-color, making them ideal for statement pieces.
- Fire Agates: Recognized for their iridescent fire-like patterns, perfect for intricate carvings and jewelry.
- Display and Decoration: Both serve as stunning focal points in home décor, accentuating elegance and sophistication.
Understanding the geological uniqueness and aesthetic appeal of these gems enhances your appreciation and informs your selection for decorative purposes, ensuring you make informed, valuable additions to your collection.
Care and Maintenance
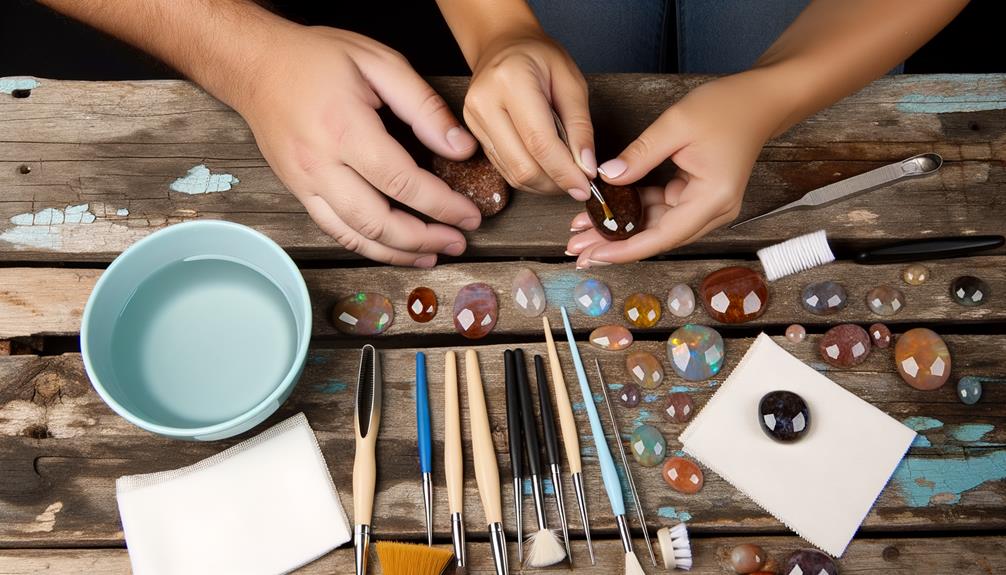

While both chocolate opals and fire agates are stunning, their care and maintenance require distinct approaches due to their unique physical properties. Chocolate opals, with their high water content, are prone to dehydration and cracking. Store them in a cool, humid environment and avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. Fire agates, known for their hardness, demand regular cleaning to maintain their luster. Use a soft brush and mild soap solution.
| Gemstone | Key Property | Environmental Care | Cleaning Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chocolate Opal | High Water Content | Cool, Humid Conditions | Avoid harsh chemicals |
| Fire Agate | Hardness | Avoid extreme temperature | Soft brush, mild soap solution |
Market Availability
In today's market, the availability of chocolate opals and fire agates varies notably due to their distinct sources and mining challenges. Chocolate opals, mainly sourced from Ethiopia, face issues such as political instability and limited mining infrastructure, which can hinder consistent supply.
Fire agates, primarily found in Mexico and the southwestern United States, require labor-intensive extraction, impacting their market presence.
Geological Distribution: Chocolate opals are largely found in volcanic regions, while fire agates are associated with hydrothermal activity.
Mining Techniques: Fire agates often require careful manual labor compared to chocolate opals, which can be more mechanized.
Supply Chain Complexity: Both stones encounter distinct logistical hurdles, but chocolate opals face more geopolitical risks.
Understanding these factors helps explain their market dynamics.
Historical Significance
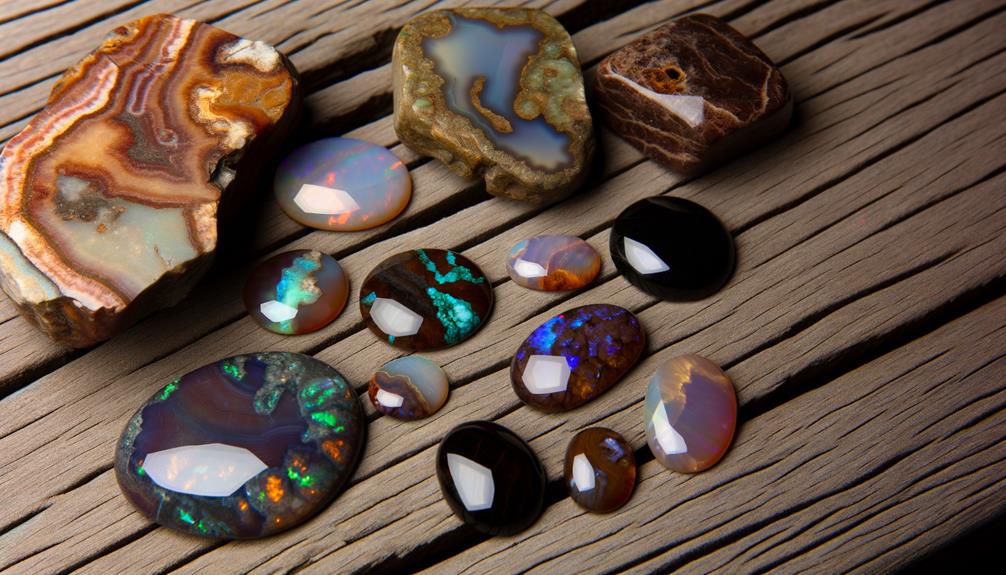

Throughout history, chocolate opals and fire agates have fascinated cultures for their unique beauty and purported mystical properties. You'll find that ancient civilizations often attributed protective and healing qualities to these stones.
Chocolate opals, with their rich brown hues, were prized by Native Australian tribes for their connection to the earth and spiritual grounding. Conversely, fire agates, known for their iridescent play of colors, were revered by indigenous Mesoamerican cultures, especially the Aztecs, for their supposed ability to ignite inner strength and courage.
Both gemstones were often used in ceremonial rituals and as amulets. Their historical significance underscores their enduring allure and cultural impact, making them much more than mere decorative items.
Conclusion
To sum up, while chocolate opals and fire agates share some similarities, they're distinct in formation, color, and patterns.
Remarkably, over 90% of the world's fire agate comes from Mexico, underscoring its geological rarity.
Understanding these differences enhances your appreciation and proper care of these unique gemstones.
With their specific physical properties and diverse uses, chocolate opals and fire agates remain fascinating subjects for both collectors and geologists.






