Fire Opals: Origins and Sources
Fire opals are mesmerizing gemstones renowned for their vibrant hues ranging from reds to yellows, caused by iron oxides within their silica-rich volcanic origin. Formed through volcanic activity, these opals consist of hydrated silica and trace elements.
Unlike other opals, they're often transparent or translucent and lack the ‘play-of-color' seen in their counterparts. Major sources include Mexico's Querétaro region, with mining methods varying from traditional to modern techniques.
Evaluating quality involves gauging color strength, clarity, and inclusions. Their rich history and unique optical properties make fire opals a fascinating subject to explore further.
Key Takeaways
- Fire opals are gemstones known for their vibrant color spectrum, typically ranging from reds to yellows.
- They form in silica-rich lava flows through volcanic activity and consist mainly of hydrated silica.
- Unlike other opals, fire opals are often transparent or translucent and do not exhibit the 'play-of-color' phenomenon.
- Mexico, particularly the Querétaro region, is the most significant source of fire opals.
- Fire opals symbolize passion, creativity, and protection in various cultures and are valued for their unique optical properties.
History of Fire Opals

Dating back to antiquity, fire opals have been prized for their vibrant play of colors and unique optical properties, enchanting gem enthusiasts and scientists alike.
In ancient Mesoamerica, the Aztecs and Mayans revered fire opals, incorporating them into religious ceremonies and ornate jewelry. You'll find that these gemstones were believed to possess mystical powers, symbolizing passion and the creative force.
European explorers brought fire opals back to the Old World, where they captivated Renaissance jewelers.
In the 19th century, renewed interest emerged with discoveries in Mexico, propelling fire opals into the global gem market.
Today, fire opals continue to be highly valued, not just for their aesthetic appeal but also for their unique physical and chemical characteristics.
Geological Formation
You'll find that fire opals originate from volcanic regions, where silica-rich water interacts with volcanic ash.
Their vivid colors result from the diffraction of light within their hydrated amorphous structure.
Understanding the mineral composition and formation process will reveal how these unique gemstones come to possess their fiery brilliance.
Volcanic Origin
Fire opals owe their enchanting hues to the volcanic processes that forge them in silica-rich lava flows. When volcanic activity occurs, it propels silica-rich fluids into voids and cracks within the cooling lava.
These fluids gradually solidify, forming opals through a process called deposition. High temperatures and pressures in volcanic environments accelerate this crystallization process, leading to the creation of vibrant fire opals.
You'll find these opals mainly in regions with historic volcanic activity, such as Mexico and Australia. The intense heat and dynamic geological movements contribute to the opal's unique play of colors, making each gem distinct.
Understanding this formation mechanism helps you appreciate the remarkable natural events that produce these stunning gemstones.
Mineral Composition
The mineral composition of fire opals primarily consists of hydrated silica (SiO₂·nH₂O), which incorporates varying amounts of water within their crystalline structure. This unique composition gives fire opals their vibrant play-of-color and translucency. The water content can range from 3% to 21%, affecting properties like density and refractive index.
To understand the specific components:
| Component | Chemical Formula | Typical Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrated Silica | SiO₂·nH₂O | 79-97 |
| Water | H₂O | 3-21 |
| Trace Elements | Various | <1 |
You'll find trace elements, such as aluminum and iron, contributing to the opal's structural integrity and color variations. By studying these elements, you gain insight into the gem's unique optical properties.
Formation Process
Understanding the formation process of fire opals requires examining the intricate interplay between volcanic activity, silica-rich water percolation, and the subsequent deposition within geological cavities.
When volcanic eruptions occur, they create a hostile environment filled with silica particles. Over time, water, rich in dissolved silica, percolates through the porous volcanic ash and rock. This silica-laden water then finds its way into voids and cavities within the volcanic rock formations.
As the water evaporates, it leaves behind concentrated silica deposits, gradually forming opal. The distinct coloration of fire opals arises due to the presence of trace elements like iron and the size and distribution of silica spheres.
This geological process creates the vibrant and mesmerizing hues characteristic of fire opals.
Key Characteristics

When examining fire opals, you'll notice their vibrant color spectrum, ranging from vivid reds to bright oranges and yellows, caused by trace amounts of iron.
Their unique transparency levels vary, with specimens ranging from completely transparent to opaque.
Additionally, common inclusions such as dendrites or tiny gas bubbles often influence their visual appeal and structural integrity.
Vibrant Color Spectrum
With a striking range of hues from fiery reds to vibrant oranges and intense yellows, fire opals exhibit a unique play-of-color phenomenon due to their specific internal structure and silica composition. The color spectrum arises from the diffraction of light within the microscopic silica spheres, each varying in size and arrangement. This diffraction causes visible light to split into spectral colors, producing a mesmerizing visual effect.
Rich, intense reds symbolize high iron content and strong light diffraction.
Vibrant oranges are indicative of a balanced silica-water ratio, enhancing color saturation.
Bright yellows result from lower iron concentrations, reflecting specific wavelengths of light.
These characteristics make fire opals visually stunning and scientifically intriguing, enchanting gem enthusiasts and geologists alike.
Unique Transparency Levels
Fire opals possess varying transparency levels, ranging from completely opaque to highly translucent, which greatly influences their overall aesthetic and quality. When you examine fire opals, you'll notice that higher translucency often enhances the stone's vibrant color play, making it more visually striking.
This transparency is due to the arrangement and size of silica spheres within the opal's structure, affecting how light interacts with the gem.
In highly translucent fire opals, light penetration creates an internal glow, amplifying the gem's fiery hues. Conversely, opaque fire opals exhibit a more solid appearance, with color concentrated on the surface.
Understanding these transparency variations helps you appreciate the diverse beauty and value of fire opals, making them unique among gemstones.
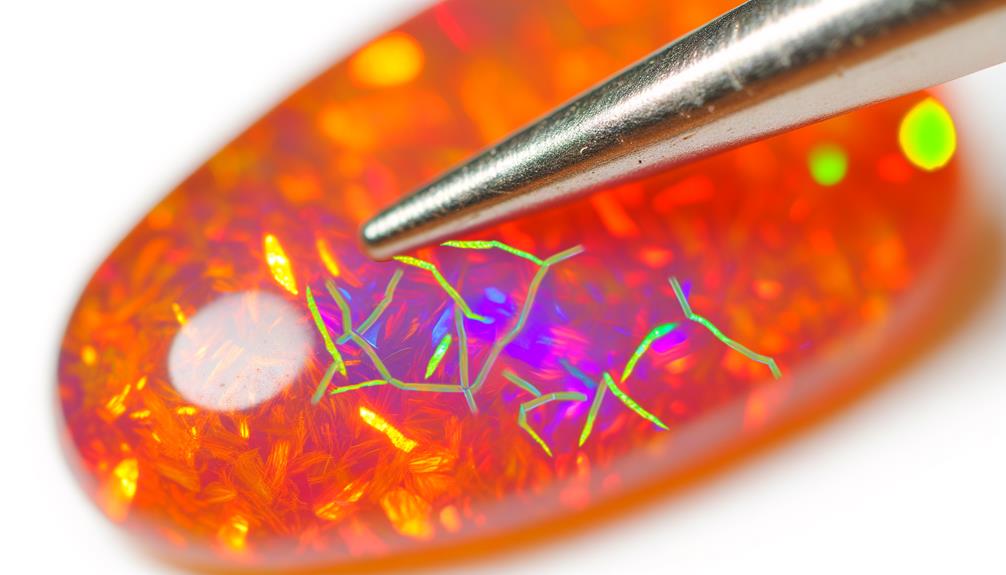
Common Inclusions Types
In addition to their varying transparency levels, fire opals often contain common inclusions like dendrites, gas bubbles, and mineral inclusions, which can affect their overall appearance and value. These inclusions arise from the geological processes that form fire opals, leading to unique internal structures.
- Dendrites: These are tree-like inclusions of manganese or iron oxides, creating intricate patterns within the opal.
- Gas Bubbles: Trapped during the opal's formation, they can create interesting light interactions but may also weaken the stone.
- Mineral Inclusions: Tiny embedded minerals, such as quartz or pyrite, can add character but sometimes detract from the gem's clarity.
Understanding these inclusions helps you appreciate and evaluate fire opals more accurately.
Color Variations
Although fire opals are renowned for their brilliant play-of-color, their base hues can range from vibrant reds and oranges to more subdued yellows and browns, each influenced by the presence of trace elements like iron and magnesium.
You'll find that iron commonly imparts a reddish tint, while magnesium can lead to more yellowish tones. The color saturation of fire opals is directly related to the concentration of these elements. Higher iron levels typically produce more intense reds, whereas lower concentrations might yield softer shades.
Additionally, the internal structure of silica spheres within the opal matrix can affect light diffraction, further enhancing or muting the stone's inherent color. Understanding these variations requires analyzing both chemical composition and physical structure.
Major Sources
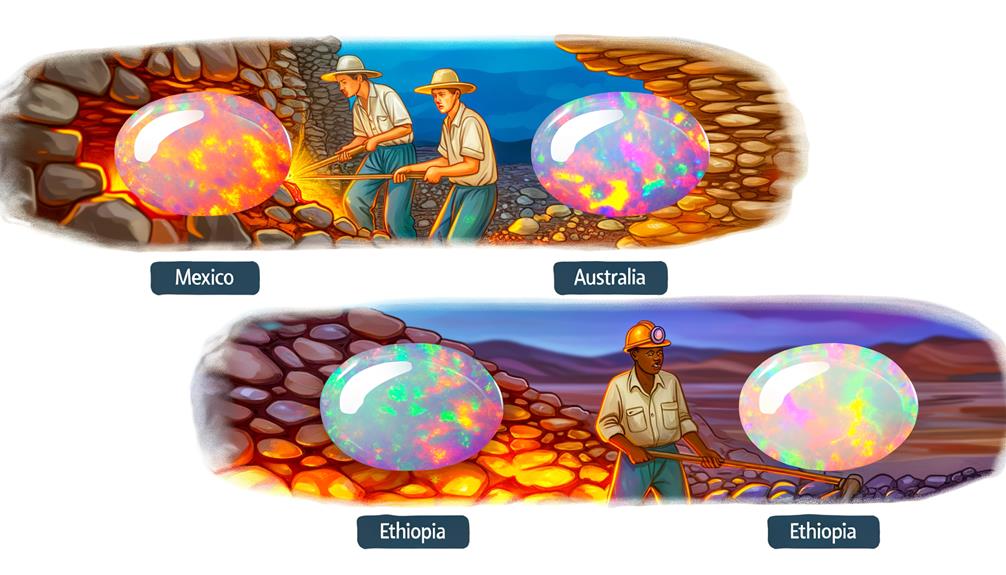
When examining the origins of these alluring gemstones, Mexico stands out as the most significant source of high-quality fire opals, particularly from the Querétaro region, where unique geological conditions foster their formation. The region's volcanic activity contributes to the creation of these vibrant stones by providing an ample supply of silica-rich water necessary for opalization.
Other notable sources include:
- Australia: Known for its diverse opals, including some fire opals, found primarily in the Lightning Ridge area.
- United States: Idaho and Nevada produce fire opals, often characterized by their intense orange hues.
- Ethiopia: Recent discoveries have revealed deposits in the Wollo Province, offering a spectrum of colors and a distinct play of light.
Understanding these sources helps appreciate the geological diversity contributing to fire opal formation.
Mining Techniques
You'll explore mining techniques for fire opals by examining the use of traditional hand tools and modern machinery.
Assess how these methods impact extraction efficiency and gemstone quality.
Traditional Hand Tools
To extract fire opals, miners often rely on traditional hand tools like pickaxes and chisels, which allow for precise and controlled removal of the delicate gemstone without causing damage. These tools are essential for maintaining the integrity of fire opals, as their fragile structure can be easily compromised by more aggressive methods.
When using these tools, you need to focus on the following:
- Pickaxes: Used to break apart larger rock formations, enabling access to opal-bearing seams.
- Chisels: Employed for fine, detailed work to carefully extract opals from their matrix.
- Hammers: Utilized to drive chisels with controlled force, ensuring minimal impact on the gemstones.
Modern Machinery Use
Modern machinery, such as hydraulic excavators and drilling rigs, greatly enhances the efficiency and scalability of fire opal mining operations.
You can use hydraulic excavators to remove large quantities of overburden quickly, exposing deeper opal-bearing strata.
Drilling rigs allow precise borehole creation, enabling you to assess the subsurface geology and target specific opal deposits.
Advanced machinery also supports continuous operation, minimizing downtime.
Automated loaders and conveyor belts streamline material handling, reducing manual labor.
Moreover, water jets and diamond-tipped saws improve the extraction process, ensuring minimal damage to the opals.
Environmental Impact Analysis
While advanced machinery optimizes fire opal mining efficiency, it's vital to scrutinize the environmental repercussions of these techniques. The extraction process often involves heavy machinery that can lead to significant ecological disturbances. For instance, these activities can disrupt local ecosystems and contribute to soil erosion. Additionally, the use of chemicals in processing can lead to contamination of nearby water sources.
Consider the following environmental impacts:
- Deforestation: Removing vegetation to access opal deposits disrupts habitats.
- Water Pollution: Chemical runoff from the mining site can contaminate rivers and groundwater.
- Air Quality: Dust and emissions from machinery can degrade air quality, affecting both wildlife and human health.
Understanding these impacts helps you advocate for more sustainable mining practices.
Fire Opals Vs. Other Opals
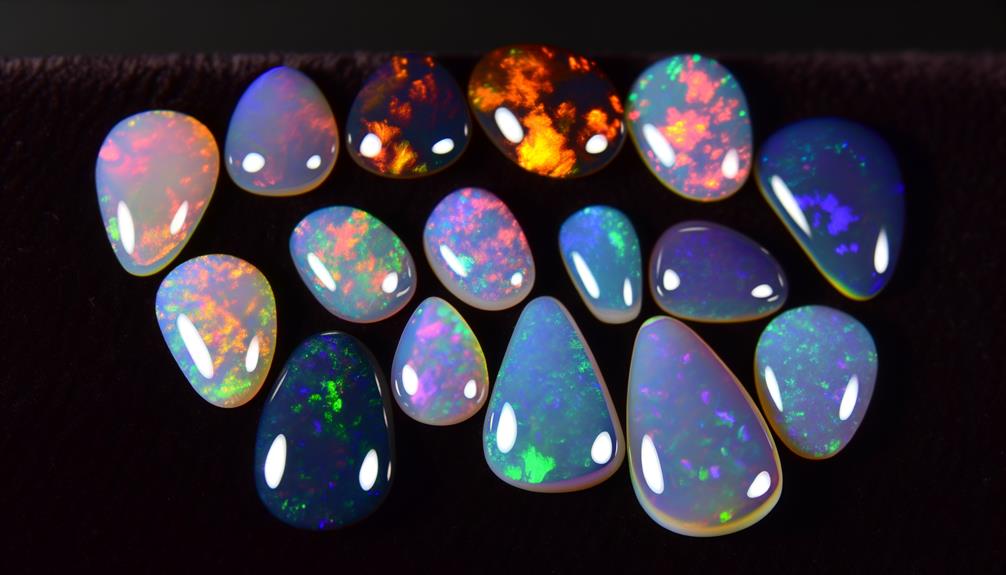
Fire opals, unlike their more commonly known counterparts, possess a unique play of color due to their distinct internal structures and chemical compositions.
You'll find that fire opals display a bright, fiery hue, mainly orange, red, or yellow, attributed to the presence of iron oxides. This differs from the typical opal, which exhibits a play of colors through diffraction of light by silica spheres within the stone.
Unlike other opals that mainly showcase iridescence, fire opals' vibrant colors come from their base material. They're typically more transparent or translucent than other opals, enhancing their brilliance.
The absence of a 'play-of-color' phenomenon in some fire opals sets them further apart, making their fiery body color a primary feature.
Grading and Quality
Evaluating the grading and quality of fire opals involves examining factors such as color strength, clarity, and the presence of any inclusions or imperfections.
You'll need to assess the saturation of the gemstone's hue, focusing on the depth of its orange to red range. High-quality fire opals exhibit outstanding clarity, allowing light to pass through without distortion.
Additionally, you should inspect for inclusions, which are internal flaws or foreign particles that can diminish the gem's value.
Understanding these criteria guarantees precise fire opal evaluations.
Uses in Jewelry

Incorporating fire opals into jewelry designs leverages their unique optical properties and vibrant hues to create standout pieces. You'll find that the stone's play-of-color, resulting from silica spheres diffracting light, enhances its allure.
Jewelers often set fire opals in rings, pendants, and earrings where the stone's fiery brilliance can be showcased. The stone's Mohs hardness of 5.5-6.5 requires careful handling to avoid scratches. When designing, consider bezel settings to protect the gem's edges.
Fire opals work well with both contemporary and traditional designs, complementing metals like gold and silver. Their vivid orange to red hues make them ideal for statement pieces, ensuring the jewelry captures attention and reflects light dynamically.
Care and Maintenance
To maintain the vibrant allure of your fire opal jewelry, it's important to understand the specific care techniques required due to the stone's relatively lower Mohs hardness and sensitivity to environmental factors. Fire opals, rated 5.5 to 6.5 on the Mohs scale, are susceptible to scratching and fracturing.
Avoid exposing them to sudden temperature changes, which can cause thermal shock and cracking.
To ensure longevity:
- Store in a soft cloth: Prevent abrasions by keeping them away from harder gemstones.
- Regular hydration: Soak in water for a few hours occasionally to prevent dehydration and maintain translucence.
- Gentle cleaning: Use lukewarm soapy water and a soft brush, avoiding harsh chemicals that could harm the stone.
Adhering to these practices will help preserve your fire opal's beauty.
Buying Tips

When buying fire opals, it is important to scrutinize the stone's clarity, color, and cut to determine its quality.
Evaluate the clarity by checking for inclusions, as high-quality fire opals are typically transparent or translucent.
The color should be vivid, with a bright, intense hue; the most sought-after fire opals display a range of warm tones from yellow to deep orange-red.
Assess the cut for symmetry and polish, ensuring it maximizes the opal's play-of-color and brilliance.
Additionally, examine the opal's body tone, as a lighter body tone can enhance the vibrant play-of-color.
Don't forget to verify the origin and certification, as these factors can greatly influence the stone's value and authenticity.
Famous Fire Opals
Renowned for their striking beauty and rarity, famous fire opals like the 'Sunglow' from Mexico exhibit an extraordinary play-of-color that captivates gem enthusiasts and collectors alike. Fire opals are characterized by their vibrant hues and unique optical properties, often displaying vivid flashes of red, orange, and yellow due to their internal structure.
These gems are formed in volcanic regions where water percolates through silica-rich lava, creating opal deposits over millennia.
Key examples include:
- 'Sunglow' Opal: Known for its intense orange hue and dynamic play-of-color.
- 'Flame Queen' Opal: Exhibits a striking red coloration with an iridescent central pattern.
- 'Mexican Sun' Opal: Celebrated for its fiery red and orange tones.
Understanding these opals' geological formation enhances appreciation of their value and allure.
Cultural Significance

Throughout history, fire opals have held significant cultural importance, symbolizing passion, creativity, and protection in various societies. The Aztecs and Mayans revered fire opals, believing they were the product of the waters of paradise. These ancient cultures used them in rituals to invoke divine favor and artistic inspiration.
In modern metaphysical practices, fire opals are considered to enhance intuition, boost self-confidence, and safeguard against negative energies.
Scientifically, the vibrant play-of-color in fire opals stems from their internal silica structure, which diffracts light. This optical phenomenon has fascinated humans for centuries, attributing almost magical properties to the gemstone.
Understanding the cultural significance of fire opals offers you deeper insight into how natural phenomena influence human belief systems and artistic expression.
Conclusion
To wrap it up, understanding fire opals can feel like discovering a new level in a video game.
You've explored their rich history, unique geological formation, and stunning color variations.
You've also learned about the major sources, and the meticulous care they require.
Armed with buying tips and an appreciation for famous fire opals, you're now ready to make an informed decision.
Remember, these gems aren't just beautiful; they're scientifically fascinating and culturally significant.






