Ethiopian Precious Fire and Common Opals: A Geology Guide
Ethiopian opals originate in the Wollo and Shewa regions, formed through volcanic activity. These opals develop in rhyolite cavities from silica-rich fluids.
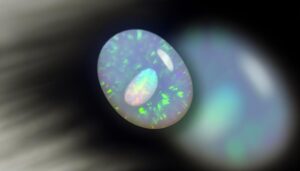
Precious fire opals display vivid play-of-color due to microscopic silica spheres, with hues like red, orange, and yellow, while common opals, although lacking this play-of-color, present diverse colors such as milky white, blue, and green. The hydrophane variety can absorb water, altering appearance.
High geothermal activity aids in the rapid formation of these unique opals. Learn about their formation, geological traits, and types to understand their distinct characteristics better.

Key Takeaways
- Ethiopian opals form in volcanic rock cavities due to silica deposition from geothermal fluids.
- Precious fire opals exhibit vivid play-of-color and transparency in reds, oranges, and yellows.
- Common opals lack play-of-color and come in hues like milky white, blue, pink, and green.
- Hydrophane opals can absorb water, changing their transparency and color.
- Trace elements in volcanic ash contribute to the varied hues of Ethiopian opals.
Origins of Ethiopian Opals

Ethiopian opals originate primarily from the Wollo and Shewa regions, where geological conditions have fostered the formation of these unique gemstones.
You'll find that volcanic activity in these regions has played a pivotal role. The opals form in the cavities of volcanic rocks, specifically rhyolites. Over time, silica-rich fluids seep into these cavities and, through a process of silica deposition, create the opals.
Studies indicate that the unique play-of-color in Ethiopian opals is due to the microscopic silica spheres arranged in a regular pattern. Additionally, the hydrophane nature of these opals, meaning they absorb water, contributes to their distinctive characteristics.
Types of Ethiopian Opals
When examining Ethiopian opals, you'll encounter two main types: precious opals and common opals.
Precious opals display a unique play-of-color due to their internal structure, while common opals lack this optical phenomenon.
Understanding these characteristics can help you differentiate between the varieties and appreciate their distinct properties.
Precious Opal Characteristics
In examining the characteristics of precious opals, you'll find that Ethiopian opals are broadly categorized into three main types: hydrophane, crystal, and black opals.
Hydrophane opals are notable for their ability to absorb water, which can enhance their play-of-color but requires careful handling.
Crystal opals exhibit a translucent to transparent body with vibrant color flashes, making them highly prized.
Black opals, rarer and more valuable, feature a dark body tone that accentuates their fiery play-of-color.
These opal types are distinguished by their unique optical properties, which are a result of their internal silica structure. Understanding these characteristics allows for better appreciation and handling of Ethiopian precious opals, ensuring their beauty and value are maintained.
Common Opal Varieties
Beyond the world of precious opals, you'll encounter a diverse range of common opal varieties in Ethiopia, each offering unique characteristics and distinct geological formations.
Analytically, common opals lack the play-of-color seen in precious opals but exhibit fascinating hues such as milky white, blue, pink, and green.
Remarkably, hydrophane opals, which are porous and can absorb water, are prevalent. They alter their transparency and color when hydrated, providing an intriguing subject for study.
Additionally, hyalite opals, often clear or faintly colored, display fluorescence under UV light. Geological evidence points to their formation in volcanic environments, specifically within rhyolitic and basaltic host rocks.
These varieties expand your understanding of opal's mineralogical diversity and geological significance.
Precious Fire Opals
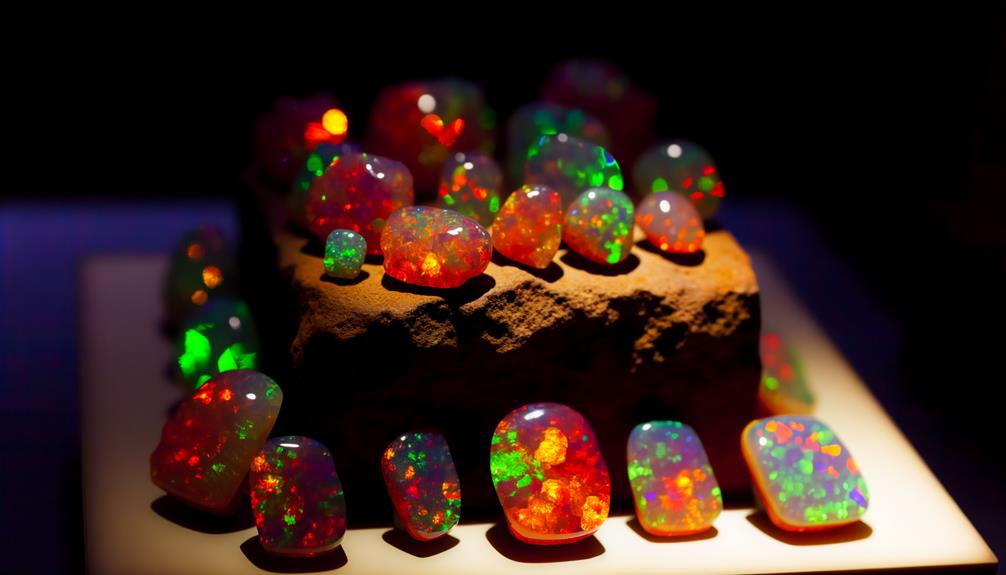

Among the varieties of Ethiopian opals, precious fire opals stand out due to their vivid play-of-color and remarkable transparency, making them highly sought after by gem enthusiasts and jewelers alike.
You'll find that these opals exhibit a broad spectrum of colors, including reds, oranges, and yellows, resulting from diffraction of light through their microstructure. Analyzing their composition, these opals often contain higher water content, enhancing their brilliance but requiring careful handling to prevent dehydration.
Studies indicate that the Wollo Province is a significant source, producing specimens with superior clarity and intensity. When evaluating precious fire opals, consider factors like body tone, color saturation, and pattern uniformity to gauge their quality accurately.
Common Opals
While precious fire opals captivate with their vivid play-of-color, common opals offer a more subdued yet equally fascinating array of hues and patterns, marked by their non-play-of-color characteristics. These opals, often overlooked, provide an array of benefits and unique features.
- Color Variability: Ranges from white, yellow, and brown to green, red, and blue.
- Transparency: Varies from opaque to translucent, adding depth and intrigue.
- Texture: Exhibits smooth, waxy surfaces or fibrous structures.
- Durability: Lower water content makes them less prone to cracking.
- Availability: More abundant and affordable compared to precious opals.
Incorporating these features into your collection can offer a rich, yet subtle beauty, showcasing the geological diversity of Ethiopian opals.
Geological Formation
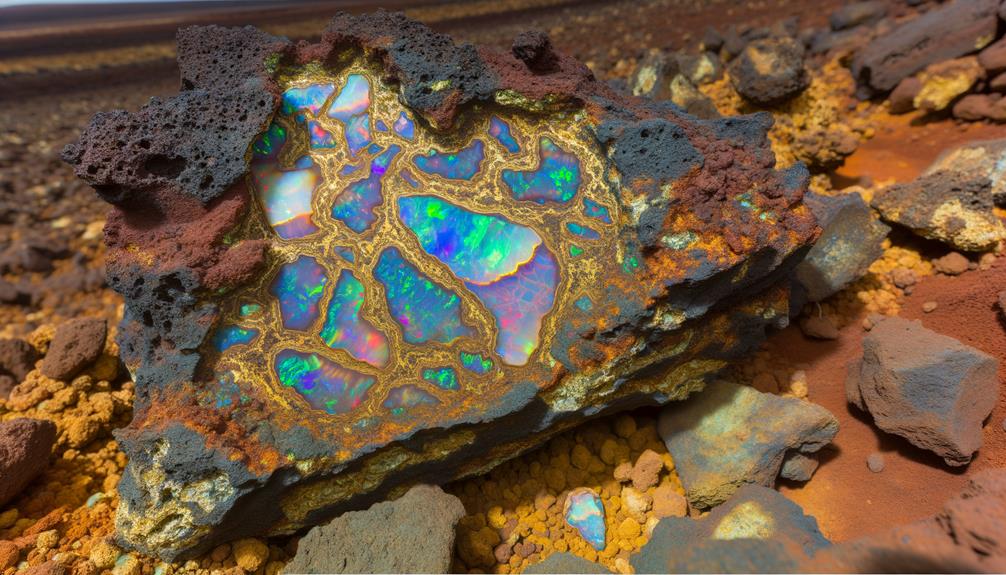

Ethiopian opals form through the gradual deposition of silica-rich solutions within volcanic ash layers, resulting in their distinct and vibrant structures.
When volcanic ash interacts with water, it creates a silica gel. Over time, this gel hardens, trapping water within the silica matrix.
You'll find that the unique play-of-color in precious opals arises from the diffraction of light through the microscopic silica spheres. Analytical studies confirm that the silica spheres' uniformity and arrangement are essential for this optical phenomenon.
Moreover, the region's geothermal activity accelerates the opalization process by continuously supplying silica-rich fluids.
Geochemical analyses show that trace elements within the volcanic ash contribute to the opals' varied hues, enhancing their aesthetic and commercial value.
Mining Regions
You'll find that the primary mining regions for Ethiopian opals are in the Wollo and Shewa provinces. These locations are rich in silica deposits, which are essential for opal formation, influenced by the volcanic activity in the area.
Extraction techniques primarily involve artisanal mining, utilizing hand tools to carefully remove the opals from the host rock.
Major Mining Locations
The primary mining locations for opals in Ethiopia are concentrated in the Wollo and Shewa regions. These areas are significant due to their geological settings, fostering the formation of high-quality opals. You'll find that the Wollo region has garnered attention for its vivid, multi-colored fire opals, while Shewa is known for its substantial deposits of common opal.
Key attributes of these mining locations include:
- Geological diversity: Varied rock formations contribute to opal genesis.
- Deposit richness: Both regions exhibit high concentrations of opal.
- Accessibility: Mining infrastructure and accessibility impact extraction efficiency.
- Environmental factors: Local climate and water availability influence mining operations.
- Economic impact: These regions support local economies through mining activities.
Analyzing these factors provides insight into the opal mining landscape in Ethiopia.
Geological Formation Factors
Understanding the geological formation factors in Ethiopia's opal mining regions requires analyzing the specific environmental and geological conditions that foster opal creation.
You need to examine the volcanic activity in these areas, as opals typically form in rhyolitic deposits. The high silica content in volcanic ash and the presence of water play pivotal roles.
When volcanic ash layers interact with groundwater, silica-rich solutions precipitate within cavities, forming opals over time. Additionally, the region's tectonic activity influences the formation by creating fractures and voids, ideal for opal deposition.
The climate's influence, particularly seasonal rainfall, helps in the cyclic dissolution and deposition processes.
Extraction Techniques Used
In Ethiopia's opal mining regions, miners employ a combination of traditional manual methods and modern mechanized techniques to extract the valuable gemstones from the earth. By utilizing both approaches, they maximize efficiency and gemstone recovery.
Traditional methods often involve hand tools for digging and sifting, while mechanized techniques use advanced machinery for deeper and larger-scale mining operations.
Key extraction techniques include:
- Manual digging: Miners use picks and shovels for surface-level excavation.
- Sifting: Handheld sieves are employed to separate opals from soil and debris.
- Drilling rigs: Machines drill deep boreholes to access opal-rich layers.
- Hydraulic mining: Water jets dislodge opal-bearing materials.
- Transport systems: Conveyors and trucks move extracted opals to processing areas.
These methods guarantee effective and sustainable opal extraction.
Market Demand
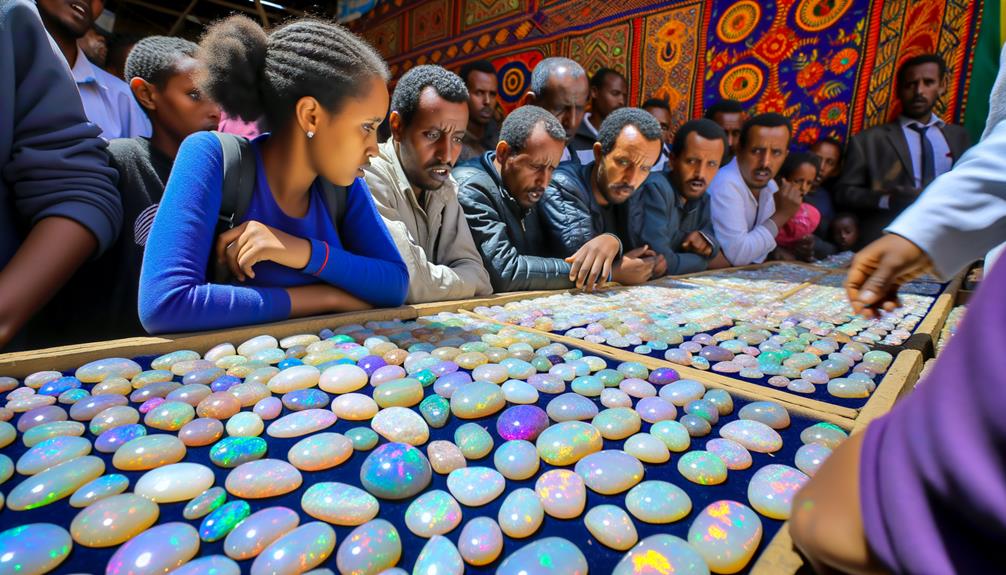

Ethiopian opals' market demand is driven by their unique play-of-color and affordability compared to other opals. You'll find that these opals exhibit a broad spectrum of vivid colors, making them highly sought after by jewelers and collectors. Market analysis shows that the affordability factor—owing to abundant deposits—significantly boosts their popularity.
Data indicates a steady increase in global demand, with the United States and Asia being primary markets. Reports from gem trade shows highlight a growing preference for Ethiopian opals over Australian ones due to their vibrant patterns and competitive pricing.
If you're looking to invest, consider that Ethiopian opals offer a high return on investment, attributed to their rising popularity and market penetration.
Care and Maintenance
Given the growing market demand, it's important to understand that proper care and maintenance of Ethiopian opals safeguard their longevity and sustained brilliance. These opals are hydrophane, meaning they readily absorb water and other liquids, which can affect their appearance and durability.
To preserve their quality, consider the following evidence-based guidelines:
- Avoid exposure to water: Hydrophane opals can change color or crack when exposed to water.
- Store in a dry environment: Use a silica gel packet to maintain a low-humidity storage condition.
- Clean with a soft cloth: Avoid using ultrasonic cleaners or harsh chemicals.
- Limit exposure to extreme temperatures: Rapid temperature changes can cause cracking.
- Regular inspection: Check for any signs of damage or color change periodically.
Adhering to these practices will safeguard your Ethiopian opals retain their beauty and value.
Conclusion
Having explored Ethiopian opals' origins, types, and geological formation, you'll see why they're enthralling the market. Precious fire opals' vibrant play-of-color and common opals' subtle beauty both hold unique appeal.
Mining regions like Wollo and Shewa are vital, fueling global demand. Proper care guarantees longevity, preserving these geological wonders. Understanding their formation from volcanic activity substantiates their extraordinary qualities, making Ethiopian opals not just gemstones, but geological treasures deserving your appreciation and investment.